HR Analytics for Organizational Restructuring
This Power BI dashboard analyzes a comprehensive Human Resources dataset to identify key drivers of employee turnover and performance disparities across departments, with critical findings about the Production department.
Project Documentation
1. Goal
To move beyond theory and apply a data-driven approach to a real-world business problem (Organizational Restructuring). The objective was to analyze an HR dataset to identify the key drivers of employee turnover and performance issues, providing actionable insights for strategic improvement.
2. Process
After evaluating several datasets, the "Human Resources Data Set" from Kaggle was selected for its relevance and quality. The data was first profiled in Excel, then loaded into Power BI. The core of the project involved scoping the analysis, creating DAX measures like TerminationPercentage, and building a series of linked visualizations (Donut, Treemap, Ribbon Chart, etc.) to construct a clear narrative around workforce composition, performance, and turnover.
3. Insights
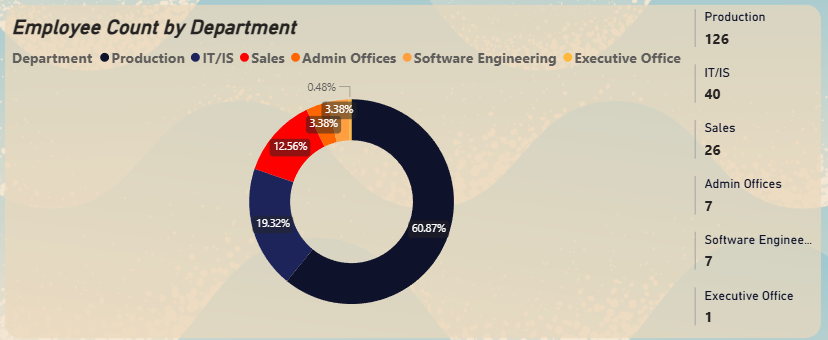
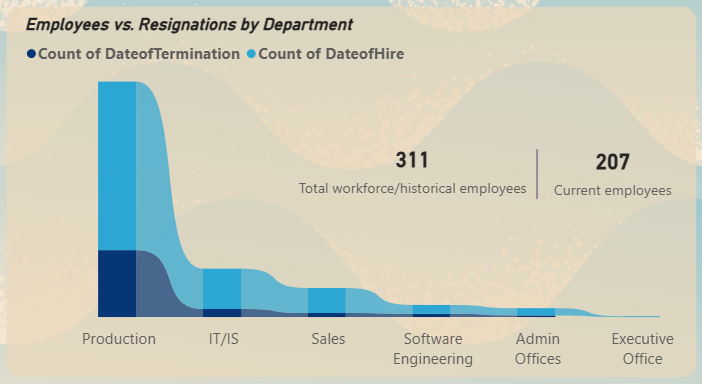
- Production Department Challenges: Despite being the largest department (60.8% of the workforce), it suffers from the lowest average performance scores and the highest turnover rate.
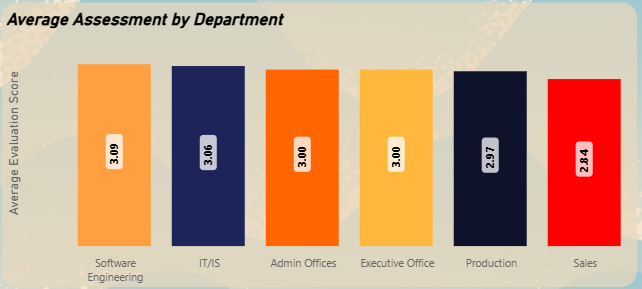
- Performance Disparity: A clear performance gap exists between departments, with Management showing the highest average performance (3.09) and Production the lowest (2.83).
- Turnover Concentration: Terminations are disproportionately concentrated in the Production department, pointing to a localized issue rather than company-wide retention problems.
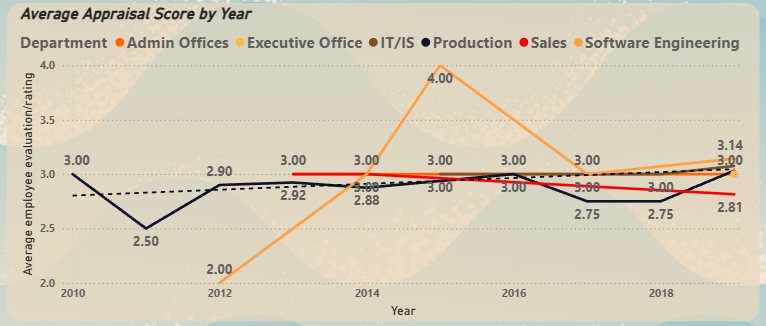
- Historical Trends: Sales department performance has been on a consistent decline since inception, while Software Engineering's performance recently dipped after a strong start.
Table of Contents
1. Project Summary
▼This case study was initiated as the practical component of a university group presentation on Organizational Restructuring Strategy. While my teammates focused on the theoretical framework, my role was to lead the data analysis, creating a case study to ground our research in real-world application. The primary objective was to apply a data-driven approach to understand the internal dynamics of a sample organization. By analyzing employee demographics, performance metrics, and termination data, the project aimed to uncover patterns that could inform strategic decisions, particularly concerning employee retention and departmental health. The key finding was a significant concentration of operational stress—high turnover and lower performance scores—within the Production department, indicating a need for targeted intervention.
2. Scope & Project Environment
▼Scope:
- The analysis focused on identifying departmental trends in employee distribution, performance, hiring, and termination.
- Key metrics included employee headcount, performance scores, tenure, engagement levels, and reasons for departure.
Project Environment:
- Tools: Microsoft Excel for initial data profiling and validation; Microsoft Power BI for data modeling, analysis, and interactive dashboard creation.
- Timeline: The project was executed over an initial two-week period, which was extended due to scheduling delays.
3. Stakeholders & Audience
▼Primary Stakeholders: University Professor (Project Sponsor), Project Teammates (Collaborators).
Primary Audience: The presentation was delivered to an academic and peer review panel, consisting of classmates and the course professor. The goal was to demonstrate the practical application of data analysis to strategic HR management, for which I received a grade of 15/15.
4. Data Sources & Data Gathering
▼Source: The analysis was conducted using the "Human Resources Data Set" available on Kaggle.
Selection Process: After considering several HR datasets, this one was chosen for its comprehensive nature and clean structure. It provided the right level of complexity for a meaningful analysis without requiring extensive cleaning.
Description: A 2020 dataset created by Drs. Carla Patalano and Rich Huebner for MBA and MSHRM programs at the New England College of Business.
Dimensions: 311 records (employees) and 36 columns.
5. Data Cleaning & Preparation
▼The dataset was found to be exceptionally clean and well-structured, a testament to its academic origin.
- Verification: Initial review in Excel to confirm data types, check for missing values, and validate categorical consistency.
- Preparation: No significant data cleaning or transformation was required prior to loading into Power BI.
6. Analysis Methodology
▼A descriptive and diagnostic analytics approach was employed to build a narrative from the data.
Scoping
▼The most challenging initial step was selecting the most impactful variables from the 36 available columns. Through an iterative process of exploration and consultation, the focus was narrowed to:
- Departments and positions
- Performance ratings
- Termination reasons
- Engagement scores
Composition Analysis
▼Understanding the current workforce distribution by department and position.
Performance Analysis
▼Assessing performance levels across different departments and tracking their trends over time.
Turnover Analysis
▼Quantifying hiring and termination rates, and diagnosing the primary reasons for employee departure.
Engagement Correlation
▼Integrating employee engagement survey data as a qualitative overlay to understand the sentiment behind turnover metrics.
7. Data Model & Relationships
▼Structure: The analysis was based on a single flat table (HRDataset_v14) loaded into Power BI. The tool's engine managed the relationships between columns implicitly.
Calculated Measures (DAX)
▼To enhance the analysis, a key performance indicator (KPI) was created using DAX:
TerminationPercentage =
DIVIDE(
COUNT(HRDataset_v14[DateofTermination]),
COUNT(HRDataset_v14[DateofHire]),
0
) * 100
Calculates the ratio of terminations to total hires, providing a standardized measure of turnover for comparison across departments of different sizes.
8. Visualization Design & Components
▼The dashboard was designed to guide the user from a high-level overview to specific, granular insights.
Donut Chart - Employee Count by Department
▼Provides an immediate view of the workforce composition, highlighting the dominance of the Production department.
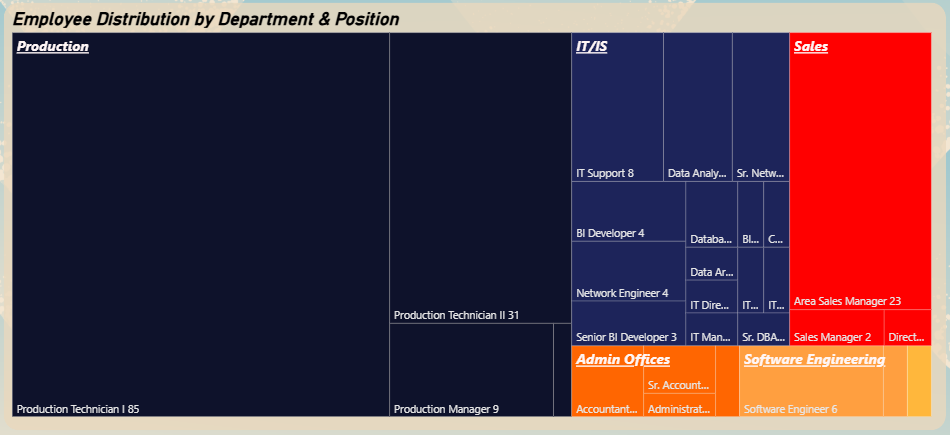
Treemap - Employee Distribution by Department & Position
▼Drills down into departmental structure, revealing the complexity and specialization within each unit.
Clustered Column Chart - Average Performance by Department
▼Compares the average performance scores across departments, identifying performance gaps.
Line Chart - Average Performance Score by Year
▼Tracks historical performance trends, showing the trajectory of each department over time.
Ribbon Chart - Hires vs. Terminations by Department
▼Visualizes the flow of talent, clearly showing which departments are net growers versus those with high churn.
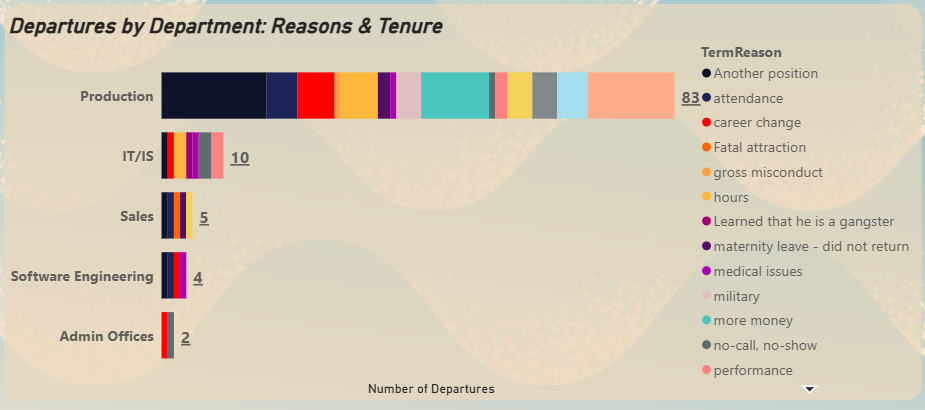
Stacked Bar Chart - Departures by Reason & Department
▼Diagnoses the root causes of turnover, with engagement scores added as a tooltip for deeper context.
9. Key Observations & Conclusions
▼Production is the Epicenter
▼The Production department is the largest, employing over 60% of the workforce. However, it also suffers from the lowest average performance scores (2.83) and, critically, the highest number of terminations (83 departures). This indicates significant operational challenges.
Performance Disparity
▼A clear performance gap exists between departments. The Management sector shows the highest average performance (3.09), while Production has the lowest. This suggests inconsistent performance management standards or varying levels of job-related pressures.
Turnover is Concentrated
▼While the IT department has the second-highest number of hires (50), terminations are disproportionately concentrated in the Production department. This points away from a company-wide retention problem and toward a localized issue requiring a targeted solution.
Insight from Trends
▼The historical performance data reveals that the Sales department has been on a consistent decline since its inception, while the Software Engineering department's performance has recently dipped after a strong start. This signals a need for proactive intervention in these areas.
10. Actionable Recommendations
▼Based on the analysis, the following strategic recommendations are proposed:
- Prioritize the Production Department: Launch a targeted initiative to investigate and improve the employee experience in Production. This could include focus groups to gather qualitative feedback, a review of working conditions, and management training programs.
- Standardize Performance Management: Investigate the performance disparity between departments. Implement a more standardized performance review and goal-setting process across the organization to ensure fairness and clarity.
- Develop Proactive Retention Strategies: Address the declining performance trend in the Sales department and the recent dip in Software Engineering before they escalate into turnover problems.
- Enhance Job Role Diversity: The analysis indicated a high concentration of specific roles in certain departments. Explore opportunities for cross-training and creating more varied career paths to improve employee engagement and reduce monotony.
11. Limitations & Future Work
▼- Static Dataset: The analysis is based on a historical snapshot. A real-time data feed would be necessary for ongoing monitoring.
- Lack of Qualitative Data: While termination reasons are provided, they are categorical. Future work should involve integrating qualitative data from exit interviews and employee surveys.
- External Factors: The analysis is internal. It does not account for external market conditions, competitor hiring, or broader economic factors that could influence turnover.
12. Challenges & Mitigations
▼Technical Presentation Constraints
▼Situation: On presentation day, I discovered the classroom PC lacked an HDMI port for my laptop and I did not have administrative rights to install Power BI on the machine.
Mitigation: I implemented a hybrid presentation strategy on the fly. A static PowerPoint version of the dashboard was displayed on the main projector for the class, while I used my laptop to provide a live, interactive demonstration to the professor and interested classmates.
Audience Comprehension
▼Situation: Partway through the presentation, it became clear that the complexity of the data was confusing some audience members.
Mitigation: I pivoted from my prepared script to a more dynamic, conversational explanation. I walked the audience through each chart's story, focusing on the "so what" of each insight.
Software Rendering Bug
▼Situation: I encountered a persistent Power BI bug that caused my carefully selected custom theme colors to render incorrectly and randomly each time the file was opened.
Mitigation: I conducted extensive troubleshooting and developed a consistent workaround: manually resetting the theme before each work session or presentation.
13. Glossary of Terms
▼- DAX (Data Analysis Expressions)
- A formula language used in Power BI to create custom calculations and measures.
- KPI (Key Performance Indicator)
- A quantifiable measure used to track and evaluate performance against strategic objectives.
- Turnover Rate
- The percentage of employees who leave an organization over a specific period.
- Churn
- Another term for employee turnover or attrition.
14. Key Skills & Tools
▼15. Project Assets & Downloads
▼For full technical documentation and implementation details, all queries, measures, and the dataset are hosted in a GitHub repository with detailed README files and inline comments:
View Repository